LearningActivities ColorBlindness
From Socr
(→Hands-on Activity) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{hidden| See the Answer| We want to estimate <math>p^2</math> and <math>\frac{X_m}{n}</math> estimates <math>p</math> so it makes sense to use <math>(\frac{X_m}{n})^2</math> as the estimator (in fact it will be the [http://wiki.stat.ucla.edu/socr/index.php/AP_Statistics_Curriculum_2007_Estim_MOM_MLE#Maximum_Likelihood_Estimation_.28MLE.29 maximum likelihood estimate]). We have <math>Var[( \frac{X_m}{n} )^2 ] = n^{-4}[E(X_m^4 ) - (E(X_m^2 ))^2 ]</math>. Take <math>q=1-p</math>. Then the fourth moment about the origin of a binomial is <math>E(X^4)= np(q-6pq^2+7npq-11np^2q+6n^2p^2q+n^3p^3)</math> and the second moment is <math>E(X^2)=np(q+np)</math>. Thus <math>Var[( \frac{X_m}{n} )^2 ] = n^{-3}(pq + 6(n-1)p^2q^2 + 4n(n-1)p^3q)</math>. }} | {{hidden| See the Answer| We want to estimate <math>p^2</math> and <math>\frac{X_m}{n}</math> estimates <math>p</math> so it makes sense to use <math>(\frac{X_m}{n})^2</math> as the estimator (in fact it will be the [http://wiki.stat.ucla.edu/socr/index.php/AP_Statistics_Curriculum_2007_Estim_MOM_MLE#Maximum_Likelihood_Estimation_.28MLE.29 maximum likelihood estimate]). We have <math>Var[( \frac{X_m}{n} )^2 ] = n^{-4}[E(X_m^4 ) - (E(X_m^2 ))^2 ]</math>. Take <math>q=1-p</math>. Then the fourth moment about the origin of a binomial is <math>E(X^4)= np(q-6pq^2+7npq-11np^2q+6n^2p^2q+n^3p^3)</math> and the second moment is <math>E(X^2)=np(q+np)</math>. Thus <math>Var[( \frac{X_m}{n} )^2 ] = n^{-3}(pq + 6(n-1)p^2q^2 + 4n(n-1)p^3q)</math>. }} | ||
| - | + | * For large samples, is it better to use a sample of men or a sample of women to estimate the probability that a randomly selected women is colorblind? Explain. | |
{{hidden| See a Hint| Show that a normal approximation is valid for both and then compare the variances.}} | {{hidden| See a Hint| Show that a normal approximation is valid for both and then compare the variances.}} | ||
Revision as of 20:12, 25 October 2011
Contents |
Distributome Learning Activities - Distributome Colorblindness Activity
Overview
This Distributome Activity illustrates an application of probability theory to study Colorblindness.
Colorblindness results from an abnormality on the X chromosome. The condition is thus rarer in women since a woman would need to have the abnormality on both of her X chromosomes in order to be colorblind (whether a woman has the abnormality on one X chromosome is essentially independent of having it on the other).
Goals
The goal of this activity is to demonstrate an efficient protocol of estimating the probability that a randomly chosen individual may be colorblind.
Hands-on Activity
Suppose that p is the probability that a randomly selected man is colorblind.
- 100 men are selected at random. What is the distribution of Xm = the number of these men that are colorblind?
- 100 women are selected at random. What is the distribution of Xf = the number of these women that are colorblind?
- To estimate the probability that a randomly selected woman is colorblind, you might use the proportion of colorblind women in a sample of n women. What is the variance of this estimator?
- Alternatively, to estimate the probability that a randomly selected woman is colorblind, you might use the square of the proportion of colorblind men in a sample of n men. Explain why this estimate makes sense. What is the variance of this estimator?
- For large samples, is it better to use a sample of men or a sample of women to estimate the probability that a randomly selected women is colorblind? Explain.
Conclusions
You can also use the delta method to find the approximate variance for the estimator above.
Translate this page:
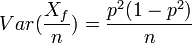 .
. 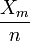 estimates
estimates 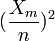 as the estimator (in fact it will be the
as the estimator (in fact it will be the ![Var[( \frac{X_m}{n} )^2 ] = n^{-4}[E(X_m^4 ) - (E(X_m^2 ))^2 ]](/distributome/uploads/math/7/b/1/7b1d064eb834c54f5fa75fccf0b68fa6.png) . Take
. Take ![Var[( \frac{X_m}{n} )^2 ] = n^{-3}(pq + 6(n-1)p^2q^2 + 4n(n-1)p^3q)](/distributome/uploads/math/a/7/5/a758430bad27ccec1ecba7e928df8764.png) .
. 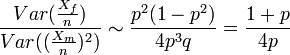 . When this ratio is greater than 1, the estimator based on the sample of men will be better. Since this happens for any
. When this ratio is greater than 1, the estimator based on the sample of men will be better. Since this happens for any 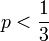 , which is clearly the case for colorblindness, it is better to use a sample of men to estimate the probability that a random woman is colorblind.
, which is clearly the case for colorblindness, it is better to use a sample of men to estimate the probability that a random woman is colorblind.