AP Statistics Curriculum 2007 Distrib Binomial
From Socr
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==[[AP_Statistics_Curriculum_2007 | General Advance-Placement (AP) Statistics Curriculum]] - Bernoulli and Binomial Random Variables and Experiments== | ==[[AP_Statistics_Curriculum_2007 | General Advance-Placement (AP) Statistics Curriculum]] - Bernoulli and Binomial Random Variables and Experiments== | ||
| - | === Bernoulli and Binomial Random Variables | + | === Bernoulli process=== |
| - | + | A Bernoulli trial is an experiment whose dichotomous outcomes are random (e.g., "success" vs. "failure", "head" vs. "tail", +/-, "yes" vs. "no", etc.) Most common notations of the outcomes of a Bernoulli process are ''success'' and ''failure'', even though these outcome labels should not be construed literally. | |
| - | <center> | + | |
| + | * Examples of Bernoulli trials | ||
| + | ** A Coin Toss. We can obverse H="heads", conventionally denoted success, or T="tails" denoted as failure. A fair coin has the probability of success 0.5 by definition. | ||
| + | ** Rolling a Die: Where the outcome space is binarized to "success"={6} and "failure" = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}. | ||
| + | ** Polls: Choosing a voter at random to ascertain whether that voter will vote "yes" in an upcoming referendum. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The Bernoulli random variable (RV): Mathematically, a Bernoulli trial is modeled by a random variable <math>X(outcome) = \begin{cases}0,& s = \texttt{success},\\ | ||
| + | 1,& s = \texttt{failure}.\end{cases}</math> If p=P(success), then the ''expected value'' of X, E[X]=p and the standard deviation of X, SD[X] is <math>\sqrt{p(1-p)}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * A '''Bernoulli process''' consists of repeatedly performing independent but identical Bernoulli trials. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Binomial Random Variables=== | ||
| + | Suppose we conduct an experiment observing an n-trial (fixed) Bernoulli process. If we are interested in the RV '''X={Number of successes in the n trials}''', then X is called a '''Binomial RV''' and its distribution is called '''Binomial Distribution'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Examples==== | ||
| + | *Roll a standard die ten times. Let X be the number of times {6} turned up. The distribution of the random variable X is a binomial distribution with n = 10 (number of trials) and p = 1/6 (probability of "success={6}). The distribution of X may be explicitely written as (P(X=x) are rounded of, you can compute these exactly by going to [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Distributions.html SOCR Distributions and selecting Binomial): | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; width:75%" border="1" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | x || 0 || 1 || 2 || 3 || 4 || 5 || 6 || 7 || 8 || 9 || 10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | P(X=x) || 0.162 || 0.323 || 0.291 || 0.155 || 0.0543 || 0.013 || 0.0022 || 0.00025 || 0.000019 || 8.269e-7 || 1.654e-8 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Suppose 10% of the human population carries the green-eye alial. If we choose 1,000 people randomly and let the RV X be the number of green-eyed people in the sample. Then the distribution of X is binomial distribution with n = 1,000 and p = 0.1 (denoted as <math>X \sim B(1,000, 0.1)</math>. | ||
===Approach=== | ===Approach=== | ||
Revision as of 19:43, 30 January 2008
Contents |
General Advance-Placement (AP) Statistics Curriculum - Bernoulli and Binomial Random Variables and Experiments
Bernoulli process
A Bernoulli trial is an experiment whose dichotomous outcomes are random (e.g., "success" vs. "failure", "head" vs. "tail", +/-, "yes" vs. "no", etc.) Most common notations of the outcomes of a Bernoulli process are success and failure, even though these outcome labels should not be construed literally.
- Examples of Bernoulli trials
- A Coin Toss. We can obverse H="heads", conventionally denoted success, or T="tails" denoted as failure. A fair coin has the probability of success 0.5 by definition.
- Rolling a Die: Where the outcome space is binarized to "success"={6} and "failure" = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- Polls: Choosing a voter at random to ascertain whether that voter will vote "yes" in an upcoming referendum.
- The Bernoulli random variable (RV): Mathematically, a Bernoulli trial is modeled by a random variable
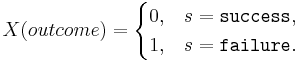 If p=P(success), then the expected value of X, E[X]=p and the standard deviation of X, SD[X] is
If p=P(success), then the expected value of X, E[X]=p and the standard deviation of X, SD[X] is 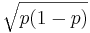 .
.
- A Bernoulli process consists of repeatedly performing independent but identical Bernoulli trials.
Binomial Random Variables
Suppose we conduct an experiment observing an n-trial (fixed) Bernoulli process. If we are interested in the RV X={Number of successes in the n trials}, then X is called a Binomial RV and its distribution is called Binomial Distribution.
Examples
- Roll a standard die ten times. Let X be the number of times {6} turned up. The distribution of the random variable X is a binomial distribution with n = 10 (number of trials) and p = 1/6 (probability of "success={6}). The distribution of X may be explicitely written as (P(X=x) are rounded of, you can compute these exactly by going to [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Distributions.html SOCR Distributions and selecting Binomial):
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| P(X=x) | 0.162 | 0.323 | 0.291 | 0.155 | 0.0543 | 0.013 | 0.0022 | 0.00025 | 0.000019 | 8.269e-7 | 1.654e-8 |
- Suppose 10% of the human population carries the green-eye alial. If we choose 1,000 people randomly and let the RV X be the number of green-eyed people in the sample. Then the distribution of X is binomial distribution with n = 1,000 and p = 0.1 (denoted as
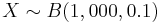 .
.
Approach
Models & strategies for solving the problem, data understanding & inference.
- TBD
Model Validation
Checking/affirming underlying assumptions.
- TBD
Computational Resources: Internet-based SOCR Tools
- TBD
Examples
Computer simulations and real observed data.
- TBD
Hands-on activities
Step-by-step practice problems.
- TBD
References
- TBD
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu
Translate this page:
