AP Statistics Curriculum 2007 Distrib RV
From Socr
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=== Random Variables=== | === Random Variables=== | ||
| - | A '''random variable''' is a function or a mapping from a sample space into the real numbers (most of the time). In other words, a random variable | + | A '''random variable''' is a function or a mapping from a sample space into the real numbers (most of the time). In other words, a random variable assigns real values to outcomes of experiments. This mapping is called ''random'', as the output values of the mapping depend on the outcome of the experiment, which are indeed random. So, instead of studying the raw outcomes of experiments (e.g., define and compute probabilities), most of the time we study (or compute probabilities) on the corresponding random variables instead. The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_variable formal general definition of random variables may be found here]. |
===Examples of random variables=== | ===Examples of random variables=== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
1,& s = \texttt{T}.\end{cases}</math>. You can see this explicit RV mapping of heads and tails to numbers in the [[SOCR_EduMaterials_Activities_BinomialCoinExperiment | SOCR Coin Experiment]]. | 1,& s = \texttt{T}.\end{cases}</math>. You can see this explicit RV mapping of heads and tails to numbers in the [[SOCR_EduMaterials_Activities_BinomialCoinExperiment | SOCR Coin Experiment]]. | ||
| - | * '''Card''': Suppose we draw a [[ | 5-card hand from a standard 52-card deck]] and we are interested in the probability that the hand contains at least one pair of cards with identical denomination. Then the sample space of this | + | * '''Card''': Suppose we draw a [[ | 5-card hand from a standard 52-card deck]] and we are interested in the probability that the hand contains at least one pair of cards with identical denomination. Then the sample space of this experiment is large - it should be difficult to list all possible outcomes. However, we can assign a random variable <math>X(s) = \begin{cases}0,& s = \texttt{no-pair},\\ |
| - | 1,& s = \texttt{at least | + | 1,& s = \texttt{at-least-1-pair}.\end{cases}</math> and try to compute the probability of P(X=1), the chance that the hand contains a pair. You can see this explicit RV mapping and the calculations of this probability at the [[SOCR_EduMaterials_Activities_CardExperiment | SOCR Card Experiment]]. |
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
* '''Probability distribution''': What is the probability of <math>P(X=x_o)</math>? For instance, in the card example above, we may be interested in [[SOCR_EduMaterials_Activities_CardExperiment#Applications | P(at least 1 pair) = P(X=1) = P(1 pair only) = 0.422569]]. Or in the die example, we may want to know P(Even number turns up) = <math>P(X \in \{2, 4, 6 \}) = 0.5</math>. | * '''Probability distribution''': What is the probability of <math>P(X=x_o)</math>? For instance, in the card example above, we may be interested in [[SOCR_EduMaterials_Activities_CardExperiment#Applications | P(at least 1 pair) = P(X=1) = P(1 pair only) = 0.422569]]. Or in the die example, we may want to know P(Even number turns up) = <math>P(X \in \{2, 4, 6 \}) = 0.5</math>. | ||
| - | * ''' | + | * '''Cumulative distribution''': <math>P(X <x_o)</math>, for all <math>x_o</math>. For instance, for the die example we have the following discrete cumulative distribution table: |
<center> | <center> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; width:75%" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; width:75%" border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | x | + | | x || 1 || 2 || 3 || 4 || 5 || 6 |
|- | |- | ||
| (P(X<=x) || 1/6 || 2/6 || 3/6 || 4/6 || 5/6 || 1 | | (P(X<=x) || 1/6 || 2/6 || 3/6 || 4/6 || 5/6 || 1 | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| - | * | + | * '''Mean/expected value''': Most natural processes may be characterized, via probability distribution of an appropriate RV, in terms of a small number of parameters. These parameters simplify the practical interpretation of the process or phenomena we study. For example, it is often enough to know what the process (or RV) ''average value'' is. This is the concept of '''expected value''' (or '''mean''') of a random variable, denoted E[X]. The expected value is the point of gravitational balance of the distribution of the RV. |
| - | + | Obviously, we may define a large number of RV for the same process. When are [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_variable#Equivalence_of_random_variables two RVs equivalent is dependent on the definition of equivalence]. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
| - | * | + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_variable Formal definition of RVs]. |
<hr> | <hr> | ||
Revision as of 02:42, 30 January 2008
Contents |
General Advance-Placement (AP) Statistics Curriculum - Random Variables and Probability Distributions
Random Variables
A random variable is a function or a mapping from a sample space into the real numbers (most of the time). In other words, a random variable assigns real values to outcomes of experiments. This mapping is called random, as the output values of the mapping depend on the outcome of the experiment, which are indeed random. So, instead of studying the raw outcomes of experiments (e.g., define and compute probabilities), most of the time we study (or compute probabilities) on the corresponding random variables instead. The formal general definition of random variables may be found here.
Examples of random variables
- Die: In rolling a regular hexagonal die, the sample space is clearly and numerically well-defined and in this case the random variable is the identity function assigning to each face of the die the numerical value it represents. This the possible outcomes of the RV of this experiment are { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }. You can see this explicit RV mapping in the SOCR Die Experiment.
- Coin: For a coin toss, a suitable space of possible outcomes is S={H, T} (for heads and tails). In this case these are not numerical values, so we can define a RV that maps these to numbers. For instance, we can define the RV
![X: S \longrightarrow [0, 1]](/socr/uploads/math/9/5/e/95e11d7a452f746b687a6e814bc71747.png) as:
as: 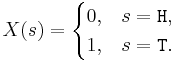 . You can see this explicit RV mapping of heads and tails to numbers in the SOCR Coin Experiment.
. You can see this explicit RV mapping of heads and tails to numbers in the SOCR Coin Experiment.
- Card: Suppose we draw a [[ | 5-card hand from a standard 52-card deck]] and we are interested in the probability that the hand contains at least one pair of cards with identical denomination. Then the sample space of this experiment is large - it should be difficult to list all possible outcomes. However, we can assign a random variable
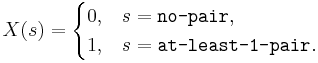 and try to compute the probability of P(X=1), the chance that the hand contains a pair. You can see this explicit RV mapping and the calculations of this probability at the SOCR Card Experiment.
and try to compute the probability of P(X=1), the chance that the hand contains a pair. You can see this explicit RV mapping and the calculations of this probability at the SOCR Card Experiment.
How do we use RVs?
There are 3 important quantities that we are always interested in when we study random processes. each of these may be phrased in terms of RVs, which simplifies their calculations.
- Probability distribution: What is the probability of P(X = xo)? For instance, in the card example above, we may be interested in P(at least 1 pair) = P(X=1) = P(1 pair only) = 0.422569. Or in the die example, we may want to know P(Even number turns up) =
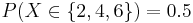 .
.
- Cumulative distribution: P(X < xo), for all xo. For instance, for the die example we have the following discrete cumulative distribution table:
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| (P(X<=x) | 1/6 | 2/6 | 3/6 | 4/6 | 5/6 | 1 |
- Mean/expected value: Most natural processes may be characterized, via probability distribution of an appropriate RV, in terms of a small number of parameters. These parameters simplify the practical interpretation of the process or phenomena we study. For example, it is often enough to know what the process (or RV) average value is. This is the concept of expected value (or mean) of a random variable, denoted E[X]. The expected value is the point of gravitational balance of the distribution of the RV.
Obviously, we may define a large number of RV for the same process. When are two RVs equivalent is dependent on the definition of equivalence.
References
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu
Translate this page:
