AP Statistics Curriculum 2007 Gamma
From Socr
Gamma Distribution
Definition: Gamma distribution is a distribution that arises naturally in processes for which the waiting times between events are relevant. It can be thought of as a waiting time between Poisson distributed events.
Probability density function: The waiting time until the hth Poisson event with a rate of change λ is
\begin{center} 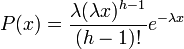 end{center}
end{center}
For X~Gamma(k,θ), where k = h and θ = 1 / λ, the gamma probability density function is given by
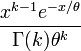
For X~Poisson(λ), the Poisson mass function is given by 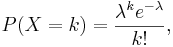 where
where
- e is the natural number (e = 2.71828...)
- k is the number of occurrences of an event - the probability of which is given by the mass function
-
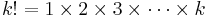
- λ is a positive real number, equal to the expected number of occurrences that occur during the given interval. For instance, if the events occur on average every 4 minutes, and you are interested in the number of events occurring in a 10 minute interval, you would use as model a Poisson distribution with λ=10/4=2.5.
