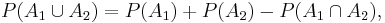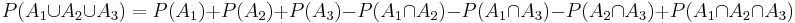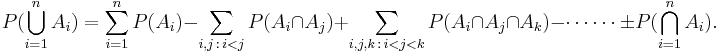AP Statistics Curriculum 2007 Prob Rules
From Socr
(Difference between revisions)
(→Addition Rule) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
For events ''A''<sub>1</sub>, ..., ''A''<sub>''n''</sub> in a probability space (S,P), the probability of the union for ''n=2'' is | For events ''A''<sub>1</sub>, ..., ''A''<sub>''n''</sub> in a probability space (S,P), the probability of the union for ''n=2'' is | ||
| - | :<math> | + | :<math>P(A_1\cup A_2)=P(A_1)+P(A_2)-P(A_1\cap A_2),</math> |
For ''n=3'', | For ''n=3'', | ||
| - | :<math> | + | :<math>P(A_1\cup A_2\cup A_3)=P(A_1)+P(A_2)+P(A_3) -P(A_1\cap A_2)-P(A_1\cap A_3)-P(A_2\cap A_3)+P(A_1\cap A_2\cap A_3)</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
In general, for any ''n'', | In general, for any ''n'', | ||
| - | :<math> | + | :<math>P(\bigcup_{i=1}^n A_i) =\sum_{i=1}^n P(A_i) |
| - | + | -\sum_{i,j\,:\,i<j}P(A_i\cap A_j) +\sum_{i,j,k\,:\,i<j<k}P(A_i\cap A_j\cap A_k)- \cdots\cdots\ \pm P(\bigcap_{i=1}^n A_i).</math> | |
| - | -\sum_{i,j\,:\,i<j} | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
=== Multiplication Rule=== | === Multiplication Rule=== | ||
Revision as of 03:54, 29 January 2008
Contents |
General Advance-Placement (AP) Statistics Curriculum - Probability Theory Rules
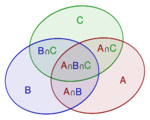
Addition Rule
The probability of a union, also called the Inclusion-Exclusion principle allows us to compute probabilities of composite events represented as unions (i.e., sums) of simpler events.
For events A1, ..., An in a probability space (S,P), the probability of the union for n=2 is
For n=3,
In general, for any n,
Multiplication Rule
Model Validation
Checking/affirming underlying assumptions.
- TBD
Computational Resources: Internet-based SOCR Tools
- TBD
Examples
Computer simulations and real observed data.
- TBD
Hands-on activities
Step-by-step practice problems.
- TBD
References
- TBD
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu
Translate this page: