Formulas
From Socr
(Difference between revisions)
John guojun (Talk | contribs) (→Transformations) |
ChinPangHo (Talk | contribs) (→Transformations) |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
* [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Kolmogorov_Distribution.html Kolmogorov-Smirnov]: <math> \!</math> | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Kolmogorov_Distribution.html Kolmogorov-Smirnov]: <math> \!</math> | ||
* [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential-power_Distribution.html Exponential Power]: <math> f(x)=(e^{1-e^{\lambda x^\kappa}})e^{\lambda x^\kappa}\lambda \kappa x^{\kappa-1}. x>0 \!</math> | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential-power_Distribution.html Exponential Power]: <math> f(x)=(e^{1-e^{\lambda x^\kappa}})e^{\lambda x^\kappa}\lambda \kappa x^{\kappa-1}. x>0 \!</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Lévy_Distribution.html Lévy distribution]: <math> L_{\alpha ,\gamma } (y)={1\over \pi } \int _{0}^{\infty }e^{-\gamma q^{\alpha } } \cos (qy) dq , y\in {\rm R} , \gamma >0 , 0<\alpha <2 </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Modified-Power-Series_Distribution.html Modified Power Series distributon]: <math> P(X=x)={a(x)\left\{u(c)\right\}^{x} \over A(c)} </math> where <math> A(c)=\sum _{x}a(x)\left\{u(c)\right\}^{x} ,a(x)\ge 0 </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Positive-binomial_Distribution.html Positive binomial distribution]: <math> P(X=x)=\binom{n}{x}{p^{x} q^{n-x} \over (1-q^{n} )} </math> where <math> x=1,2,...,n </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Basic-Lagrangian-distribution-of-the-first-kind.html Basic Lagrangian distribution of the first kind (BLD1)]: <math> P(X=x)={1\over x!} \left[{\partial ^{x-1} \over \partial z^{x-1} } (g(z))^{x} \right]_{z=0} </math> where <math> g(z) </math> is pgf , <math> g(0) </math> is not 0 | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/General-Basic-Lagrangian-distribution-of-the-first-kind.html General Basic Lagrangian distribution of the first kind (GLD1)]: <math> P(X=0)=f(0) , | ||
| + | P(X=x)={1\over x!} \left[{\partial ^{x-1} \over \partial z^{x-1} } \left\{(g(z))^{x} {\partial f(z)\over \partial z} \right\}\right]_{z=0} , x>0</math> Where f(z) and g(z) are pgf , <math>\left[{\partial ^{x-1} \over \partial z^{x-1} } \left\{(g(z))^{x} {\partial f(z)\over \partial z} \right\}\right]_{z=0} >0</math> for <math>x\ge 1</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Binomial-delta_Distribution.html Binomial-delta distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={n\over x}\binom{{mx}}{x-n}p^{x-n} q^{n+mx-x} </math> for <math>x\ge n</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Binomial-Poisson_Distribution.html Binomial-Poisson distribution]: <math> P(X=x)=e^{-M} {(Mq^{m} )^{x} \over x!} {}_{2} F{}_{0} [1-x,-mx;{p\over Mq} ] </math> , for <math>x\ge 0 </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Binomial-negative-binomial_Distribution.html Binomial-negative-binomial distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={\Gamma (k+x)\over x!\Gamma (x)} Q^{-k} \left({Pq^{m} \over Q} \right)^{x} {}_{2} F_{1} [1-x,-mx;1-x-k;{-pQ\over qP} ] </math> for <math>x\ge 0</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson-delta _Distribution.html Poisson-delta distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={n\over x} {e^{-\theta x} (\theta x)^{x-n} \over (x-n)} </math> for <math>x\ge n </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson-Poisson_Distribution.html Poisson-Poisson distribution(also called "Generalized Poisson distribution")]: <math> P(X=x)=M(M+\theta x)^{x-1} e^{-(M+\theta x)} /x! </math> for <math>x\ge 0 </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson-binomial_Distribution.html Poisson-binomial distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={(\theta x)^{x-1} \over x!} e^{-\theta x} npq^{n-1} {}_{2} F_{0} [1-x,1-n;{p\over \theta qx} ] , x\ge 1</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson-negative-binomial_Distribution.html Poisson-negative-binomial distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={(\theta x)^{x-1} \over x!} e^{-\theta x} kPQ^{-k-1} {}_{2} F_{0} [1-x,1+k;{-P\over \theta Qx} ] , x\ge 1</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial-delta_Distribution.html Negative-binomial-delta distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={n\over x} {\Gamma (kx+x-1)\over (x-n)!\Gamma (kx)} \left({P\over Q} \right)^{x-n} Q^{-kx} , x\ge n </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial-Poisson_Distribution.html Negative-binomial-Poisson distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={e^{-M} M^{x} \over x!} Q^{-kx} {}_{2} F_{0} [1-x,kx;-;{-P\over MQ} ] </math> , for <math>x\ge 0</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial-binomial_Distribution.html Negative-binomial-binomial distribution]: <math> P(X=0)=q^{n} </math> , <math>P(X=x)=npq^{n-1} {\Gamma (kx+x-1)\over x!\Gamma (kx)} \left({P\over Q} \right)^{x-1} Q^{-kx} {}_{2} F_{1} [1-x,1-n;2-x-kx;{-pQ\over Pq} ] </math> for <math>x\ge 1</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial-negative-binomial_Distribution.html Negative-binomial-negative-binomial distribution]: <math> P(X=x)=(Q')^{-M} \left({P'\over Q'Q^{k} } \right)^{x} {\Gamma (M+x)\over x!\Gamma (M)} {}_{2} F_{1} [1-x,kx;1-M-x;{PQ'\over P'Q} ] </math> for <math>x\ge 1</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Weight-binomial_Distribution.html Weight binomial distribution]: <math> P(X=x)=w(x)p_{x} /\sum _{x}^{}w(x)p_{x}</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Positive-Poisson_Distribution.html Positive Poisson distribution (conditional Poisson distribution)]: <math> P(X=x)=(e^{\theta } -1)^{-1} \theta ^{x} /x! , x=1,2,......</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Left-truncated-Poisson_Distribution.html Left-truncated Poisson distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={e^{-\theta } \theta ^{x} \over x!} \left[1-e^{-\theta } \sum _{j=0}^{r_{1} -1}{\theta ^{j} \over j!} \right]^{-1} , x=r_{1} ,r_{1} +1,...</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Right-truncated-Poisson_Distribution.html Right-truncated Poisson distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={\theta ^{x} \over x!} \left[\sum _{j=0}^{r_{2} }{\theta ^{j} \over j!} \right]^{-1} , x=0,1,...,r_{2}</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Doubly-truncated-Poisson_Distribution.html Doubly-truncated Poisson distribution]: <math> P(X=x)={\theta ^{x} \over x!} \left[\sum _{j=r_{1} }^{r_{2} }{\theta ^{j} \over j!} \right]^{-1} , x=r_{1} ,r_{1} +1,...,r_{2} , 0<r_{1} <r_{2}</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Misrecorded-Poisson_Distribution.html Misrecorded Poisson distribution]: <math> P(X=0)=\omega +(1-\omega )e^{-\theta }, P(X=x)=(1-\omega ){e^{-\theta } \theta ^{x} \over x!} , x\ge 1</math> | ||
==Transformations== | ==Transformations== | ||
| Line 148: | Line 171: | ||
* [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/HyperbolicSecant_Distribution.html Standard Cauchy to Hyperbolic Secant]: <math> \frac{log|x|}{\pi} \ </math> | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/HyperbolicSecant_Distribution.html Standard Cauchy to Hyperbolic Secant]: <math> \frac{log|x|}{\pi} \ </math> | ||
* [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard_Power.html Beta to Standard Power]: <math> \alpha=\beta, \beta=1 \ </math> | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard_Power.html Beta to Standard Power]: <math> \alpha=\beta, \beta=1 \ </math> | ||
| - | |||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal Power series to Pascal]: <math> A(c)=(1-c)^{-x}, c=1-p \ </math> | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal Power series to Pascal]: <math> A(c)=(1-c)^{-x}, c=1-p \ </math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pacal Gamma Poisson to Pascal]: <math> \alpha=(1-p)/p, \beta=n \ </math> | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pacal Gamma Poisson to Pascal]: <math> \alpha=(1-p)/p, \beta=n \ </math> | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_Poisson Poisson to Gamma Poisson]: <math> \mu \sim gamma \ </math> | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_Poisson Poisson to Gamma Poisson]: <math> \mu \sim gamma \ </math> | ||
| Line 169: | Line 187: | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geometric Pascal to geometric]: <math> n=1 \ </math> | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geometric Pascal to geometric]: <math> n=1 \ </math> | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal geometric to pascal]: <math> \sum{X_i}\ </math> | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal geometric to pascal]: <math> \sum{X_i}\ </math> | ||
| - | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geometric discrete weibull to geometric]: <math> \ </math> | + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geometric discrete weibull to geometric]: <math> \beta=1\ </math> |
| - | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal pascal to normal]: <math> \ </math> | + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal pascal to normal]: <math> \mu=n(1-p), n\to\infty\ </math> |
| - | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/standard_normal normal to standard normal]: <math> \ </math> | + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/standard_normal normal to standard normal]: <math> \mu=0, \sigma=1\ </math> |
| - | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noncentral_chi-square normal to noncentral_chi-square]: <math> \ </math> | + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noncentral_chi-square normal to noncentral_chi-square]: <math> \sum{X_i^2/{\sigma}^2}\ </math> |
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html Normal to Chi-square]: <math> (iid) \sum (\frac{x_i-\mu}{\sigma})^2\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Normal_Distribution.html Beta to Normal]: <math> \beta=\gamma \to \infty \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Normal_Distribution.html Normal to Gamma-normal]: <math> \sigma \sim Inverted \ gamma \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Cauchy_Distribution.html Standard Normal to Standard Cauchy]: <math> \frac{X_1}{X_2} \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Normal_Distribution.html Inverse Gaussian to Standard normal]: <math> \lambda \to \infty \ </math> | ||
* [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html Noncentral chi-square to Chi-square]: <math> \delta=0 \ </math> | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html Noncentral chi-square to Chi-square]: <math> \delta=0 \ </math> | ||
* [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Gamma_Distribution.html Gamma to Log gamma]:<math> log X \ </math> | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Gamma_Distribution.html Gamma to Log gamma]:<math> log X \ </math> | ||
| Line 180: | Line 203: | ||
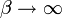
* [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/InverseGaussian_Distribution.html Inverse Gaussian to Standard Wald]:<math> \mu=1 \ </math> | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/InverseGaussian_Distribution.html Inverse Gaussian to Standard Wald]:<math> \mu=1 \ </math> | ||
* [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html Inverse Gaussian to Chi-square]:<math> \lambda(X-\mu)^2/(\mu^2 X)\ </math> | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html Inverse Gaussian to Chi-square]:<math> \lambda(X-\mu)^2/(\mu^2 X)\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Chi_Distribution.html Chi-square to Chi]:<math> \sqrt{X}\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Fisher_Distribution.html Chi-square to F]:<math> \frac{X_1/n_1}{X_2/n_2}\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html F to Chi-square]:<math> n_1 X, n_2 \to \infty \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html Exponential to Chi-square]:<math> (iid) \frac{2}{\alpha} \sum {X_i}\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential_Distribution.html Chi-square to Exponential]:<math> \alpha=2, n=2 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Erlang_Distribution.html Chi-square to Erlang]:<math> n \ even\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html Gamma to Chi-square]:<math> n=2\beta, \alpha=2 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ChiSquare_Distribution.html Beta to Standard Uniform]:<math> \beta=\gamma=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Erlang_Distribution.html Gamma to Erlang]:<math> \beta=n \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Gamma_Distribution.html Gamma to Inverted Beta]:<math> X_1/X_2, \alpha=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Beta_Distribution.html Beta to Inverted Beta]:<math> \frac{X}{1-X} \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Cauchy_Distribution.html Cauchy to Arctangent]:<math> zero \ truncate \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Erlang_Distribution.html Hypoexponential to Erlang]:<math> \vec \alpha=\alpha \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential_Distribution.html Exponential to Hypoexponential]:<math> \sum X_i\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential_Distribution.html Erlang to Exponential]:<math> n=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Gompertz_Distribution.html Makeham to Gompertz]:<math> \gamma=0 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/StudentT_Distribution.html Doubly noncentral t to Noncentral t]:<math> \gamma=0 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Fisher_Distribution.html Exponential to F]:<math> \alpha=1, X_1/X_2\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Fisher_Distribution.html Noncentral F to F]:<math> \delta \to 0\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential_Distribution.html Exponential to Hyperexponential]:<math> Mixture\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential_Distribution.html Hyperexponential to Exponential]:<math> \vec \alpha=\alpha \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential_Distribution.html IDB to Exponential]:<math>\delta=\kappa \to 0, \alpha=1/ \gamma \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Rayleigh_Distribution.html Exponential to Rayleigh]:<math> X^2\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential_Distribution.html Weibull to Exponential]:<math> \beta=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Weibull_Distribution.html Exponential to Weibull]:<math> X^{1/\beta}\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Exponential_Distribution.html Muth to Exponential]:<math> \alpha=1, \kappa \to 0 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Gompertz_Distribution.html Standard uniform to Gompertz]:<math> \frac{log[1-(log X)(log \kappa)/\delta]}{log \kappa}\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/ContinuousUniform_Distribution.html Standard uniform to Exponential Power]:<math> [log(1-log(1-X))/\gamma]^{1/\kappa}\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Laplace_Distribution.html Error to Laplace]:<math> a=0, b=\alpha/2, c=2\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Error_Distribution.html Laplace to Error]:<math> \alpha_1=\alpha_2 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Log-logistic_Distribution.html Standard uniform to log logistic]:<math> \frac{1}{\lambda}(\frac{1-X}{X})^{1/\kappa} \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard-triangular_Distribution.html Standard uniform to Standard triangular]:<math> X_1-X_2 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/uniform_Distribution.html Standard uniform to uniform]:<math> a+(b-a)X \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard-Power_Distribution.html Standard uniform to standard power]:<math> X^{1/\beta} \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard-uniform_Distribution.html Standard power to standard uniform]:<math> \beta=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard-power_Distribution.html Standard uniform to standard power]:<math> X_(n) \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard-power_Distribution.html Minimax to standard power]:<math> \gamma=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Rayleigh_Distribution.html IDB to Rayleigh]:<math> \delta=2/\alpha, \gamma=0 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard-Power_Distribution.html Power to Standard Power]:<math> \alpha=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Rayleigh_Distribution.html Weibull to Rayleigh]:<math> \beta=2 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Pareto_Distribution.html Generalized Pareto to Pareto]:<math> \gamma=0, X+\delta \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Standard-triangular_Distribution.html Triangular to standard triangular]:<math> a=-1,b=1,m=0\ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Extreme-value_Distribution.html Weibull to Extreme-value]:<math> logX \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Lomax_Distribution.html Log logistic to lomax]:<math> \kappa=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Log logistic_Distribution.html Lomax to log logistic]:<math> \kappa=1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Logistic_Distribution.html Log logistic to logistic]:<math> logX \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Triangular_Distribution.html TSP to triangular]:<math> n=2 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Uniform_Distribution.html von Mises to Uniform]:<math> \kappa \to 0 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Cauchy_Distribution.html Lévy to Cauchy]:<math> \alpha =1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Gaussian_Distribution.html Lévy to Gaussian]:<math> \alpha \to 2</math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Power-series_Distribution.html Modified Power Series to Power series]:<math> u(c)=c \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Geometric_Distribution.html BLD1 to Geometric]:<math> g(z)=1-p+pz \ </math> where<math>0<p<1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Borel-Tanner_Distribution.html BLD1 to Borel-Tanner]:<math> g(z)=e^{\lambda (z-1)} , 0<\lambda \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Binomial_Distribution.html GLD1 to Binomial]:<math> g(z)=1 \ </math> and <math>f(z)=(q'+p'z)^{n} \ </math> where <math>q'=1-p' \ </math> , <math>0<p'<1 \ </math>, and n is positive integer. | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial_Distribution.html GLD1 to Negative binomial]:<math> g(z)=1 \ </math> and <math> f(z)=(q'+p'z)^{n} \ </math> where <math> q'=1+P \ </math> , <math> 0<P \ </math> , and <math> n=-k<0 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Binomial-delta_Distribution.html GLD1 to Binomial-delta]: <math> g(z)=(q+pz)^{m} \ </math> , <math> f(z)=z^{n} \ </math> , <math> mp<1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Binomial-Poisson_Distribution.html GLD1 to Binomial-Poisson]:<math> : g(z)=(q+pz)^{m} \ </math> , <math> f(z)=e^{M(z-1)} \ </math> , <math> mp<1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Binomial-negative-binomial_Distribution.html GLD1 to Binomial-negative-binomial]:<math> g(z)=(q+pz)^{m} \ </math> , <math> f(z)=(Q-Pz)^{-k} \ </math> , <math> mp<1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson-delta_Distribution.html GLD1 to Poisson-delta]: <math> g(z)=e^{\theta (z-1)} \ </math>, <math> f(z)=z^{n} \ </math>, <math> \theta <1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson-Poisson_Distribution.html GLD1 to Poisson-Poisson]: <math> g(z)=e^{\theta (z-1)} , f(z)=e^{M(z-1)} , \theta <1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson-binomial_Distribution.html GLD1 to Poisson-binomial]: <math> g(z)=e^{\theta (z-1)} , f(z)=(q+pz)^{n} , \theta <1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson-negative-binomial_Distribution.html GLD1 to Poisson-negative-binomial]: <math> g(z)=e^{\theta (z-1)} , f(z)=(Q-Pz)^{-k} , \theta <1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial-delta_Distribution.html GLD1 to Negative-binomial-delta]: <math> g(z)=(Q-Pz)^{-k} , f(z)=z^{n} , kP<1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial-Poisson_Distribution.html GLD1 to Negative-binomial-Poisson]: <math> g(z)=(Q-Pz)^{-k} , f(z)=e^{M(z-1)} , kP<1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial-binomial_Distribution.html GLD1 to Negative-binomial-binomial]: <math> g(z)=(Q-Pz)^{-k} , f(z)=(q+pz)^{n} , kP<1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Negative-binomial-negative-binomial_Distribution.html GLD1 to Negative-binomial-negative-binomial]: <math> g(z)=(Q-Pz)^{-k} , f(z)=(Q'-P'z)^{-M} , kP<1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Poisson_Distribution.html Chi-Square to Poisson]: <math> \left(1-F_{\chi _{2(x+1)}^{2} } (2t/\tau )\right)-\left(1-F_{\chi _{2x}^{2} } (2t/\tau )\right) \ </math> and <math> \lambda =t/\tau \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Positive-Poisson_Distribution.html Left-truncated Poisson to Positive Poisson]: <math> r_{1} =1 \ </math> | ||
| + | * [http://socr.ucla.edu/htmls/dist/Right-truncated-Poisson_Distribution.html Doubly-truncated Poisson to Right-truncated Poisson]: <math> r_{1} =0 \ </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
| + | |||
* SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu | * SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu | ||
{{translate|pageName=http://wiki.stat.ucla.edu/socr/index.php?title=Formulas}} | {{translate|pageName=http://wiki.stat.ucla.edu/socr/index.php?title=Formulas}} | ||
Current revision as of 12:57, 18 January 2011
Probability Density Functions (PDFs)
- Standard Normal PDF:
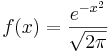
- General Normal PDF:
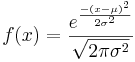
- Chi-Square PDF:
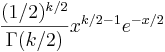
- Gamma PDF:
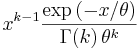
- Beta PDF:
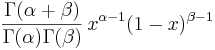
- Student's T PDF:
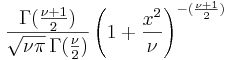
- Poisson PDF:
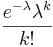
- Chi PDF:
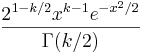
- Cauchy PDF:
![\frac{1}{\pi\gamma \left[1 + \left(\frac{x-x_0}{\gamma}\right)^2\right]}](/socr/uploads/math/a/9/2/a9260c6814d86ac3231f3934db752577.png)
- Exponential PDF:
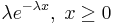
- F Distribution PDF:
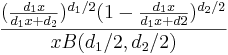
- Bernoulli PMF:
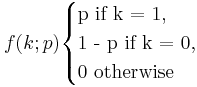
- Binomial PMF:
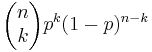
- Multinomial PMF:
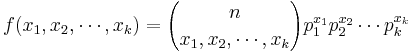 , where
, where  ,
, 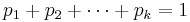 , and
, and 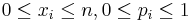 .
.
- Negative Binomial PMF:
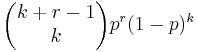
- Negative-Multinomial Binomial PMF:
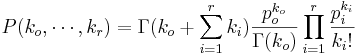
- Geometric PMF:
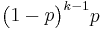
- Erlang PDF:
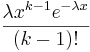
- Laplace PDF:
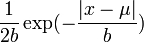
- Continuous Uniform PDF:
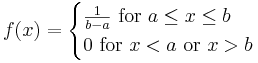
- Discrete Uniform PMF:
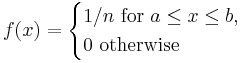
- Logarithmic PDF:
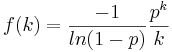
- Logistic PDF:
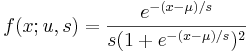
- Logistic-Exponential PDF:
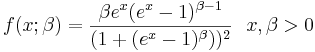
- Power Function PDF:
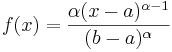
- Benford's Law:
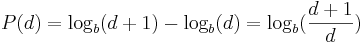
- Pareto PDF:
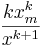
- Non-Central Student T PDF:
![f(t)=\frac{\nu^{\nu/2}e^{-\nu\mu^2/2(t^2+\nu)}} {\sqrt{\pi}\Gamma(\nu/2)2^{(\nu-1)/2}(t^2+\nu)^{(\nu+1)/2}} \times\int\limits_0^\infty x^\nu\exp\left[-\frac{1}{2}\left(x-\frac{\mu t}{\sqrt{t^2+\nu}}\right)^2\right]dx](/socr/uploads/math/e/3/7/e37a9ea8dea4ca3d0d7d55f76aaa430b.png)
- ArcSine PDF:
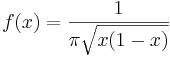
- Circle PDF:
![f(x)={2\sqrt{r^2 - x^2}\over \pi r^2 }, \forall x \in [-r , r]](/socr/uploads/math/4/5/a/45a7876ef35972bf28385be926c52b62.png)
- U-Quadratic PDF:
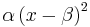
- Standard Uniform PDF:
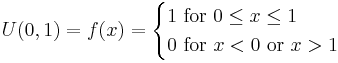
- Zipf:
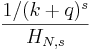
- Inverse Gamma:
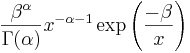
- Fisher-Tippett:
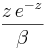
where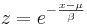
- Gumbel:
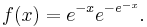
- HyperGeometric:
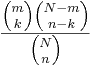
- Log-Normal:
![\frac{1}{x\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\exp\left[-\frac{\left(\ln(x)-\mu\right)^2}{2\sigma^2}\right]](/socr/uploads/math/b/3/f/b3f2a95779f28c24a5a265ba6498ceec.png)
- Gilbrats:
![\frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\exp\left[-\frac{\left(\ln(x)\right)^2}{2\sigma^2}\right]](/socr/uploads/math/d/0/3/d03d955b51d917ba307deef3c7e277a0.png)
- Hyperbolic Secant:
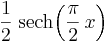
- Gompertz:
![b e^{-bx} e^{-\eta e^{-bx}}\left[1 + \eta\left(1 - e^{-bx}\right)\right]](/socr/uploads/math/4/e/f/4efe11d1016f67a67761bf1697fb5a9b.png)
- Standard Cauchy:
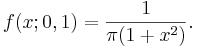
- Rectangular:
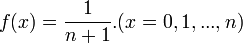
- Beta-Binomial:
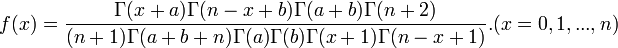
- Negative Hypergeometric:
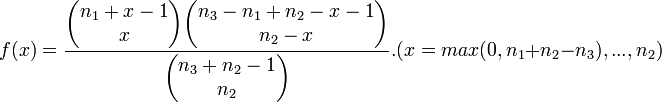
- Standard Power:
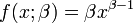
- Power_Series:
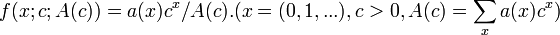
- Zeta:
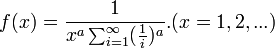
- Logarithm:
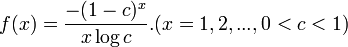
- Beta_Pascal:
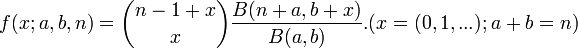
- Gamma_Poisson:
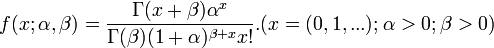
- Pascal:
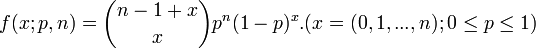
- Polya:
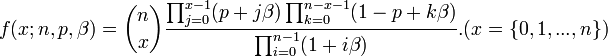
- Normal-Gamma:
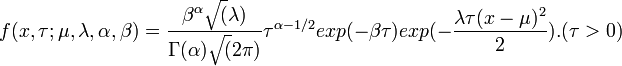
- Discrete_Weibull:
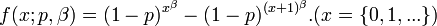
- Log Gamma:
![f(x)=[1/ \alpha^\beta \Gamma(\beta)]e^{\beta x}e^{-e^x/a}. (-\infty<x<\infty) \!](/socr/uploads/math/7/c/4/7c4a06b45d1e495c5a95fa4c34eb7e01.png)
- Generalized Gamma:
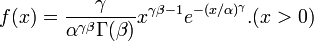
- Noncentral-Beta:
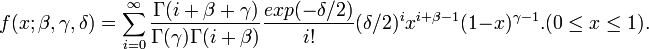
- Inverse Gausian:
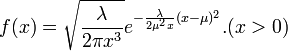
- Noncentral_chi-square:
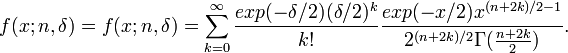
- Standard Wald:
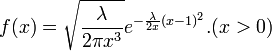
- Inverted Beta:
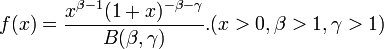
- Arctangent:
![f(x; \lambda, \phi)= \frac{\lambda}{[arctan(\lambda \phi)+\pi/2][1+\lambda^2 (x - \phi)^2]} (x \geq 0, -\infty < \lambda < \infty) \!](/socr/uploads/math/7/6/d/76da984a4dca1594e390bcd6708e18cd.png)
- Makeham:
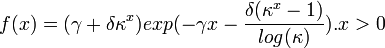
- Hypoexponential:
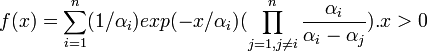
- Doubly Noncentral t:

- Hyperexponential:
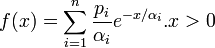
- Muth:
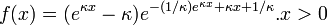
- Error:
![f(x) = \frac{exp[-(|x-a|/b)^{2/c}/2]}{b 2^{c/2+1}\Gamma(1+c/2)}. -\infty < x < \infty \!](/socr/uploads/math/6/e/4/6e42fd0f037ed8770a2702cb2d94ffe0.png)
- Minimax:
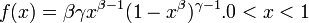
- Noncentral F:
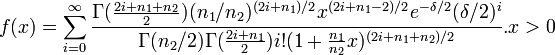
- IDB:
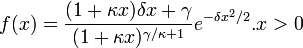
- Standard Power:
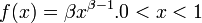
- Rayleigh:
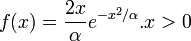
- Standard Triangular:
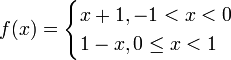
- Doubly noncentral F:
![f(x)= \sum_{j=0}^{\infty}\sum_{k=0}^{\infty}[\frac{e^{-\delta/2}(\frac{1}{2}\delta)^j}{j!}][\frac{e^{-\gamma/2}(\frac{1}{2}\gamma)^k}{k!}]\times n_1^{(n_1/2)+j}n_2^{(n_2/2)+k}x^{(n_1/2)+j-1}\times (n_2+n_1 x)^{-\frac{1}{2}(n_1+n_2)-j-k}\times [B(\frac{1}{2}n_1+j,\frac{1}{2}n_2+k)]^{-1}. x>0 \!](/socr/uploads/math/d/8/8/d888b49a4abc96cf20e931e233f1d9c7.png)
- Power:
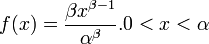
- Weibull:
![f(x)=(\beta/\alpha)x^{\beta-1}exp[-(1/\alpha)x^\beta]. x>0 \!](/socr/uploads/math/0/d/c/0dc3d3e9bdecd2f48c9af39fcc40692d.png)
- Log-logistic:
![f(x)=\frac{\lambda \kappa(\lambda x)^{\kappa-1}}{[1+(\lambda x)^\kappa]^2}. x>0 \!](/socr/uploads/math/1/c/d/1cd47902dd18fe543bc4fd2e55f98c76.png)
- TSP:
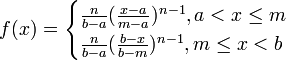
- Extreme value:
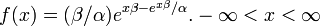
- Lomax:
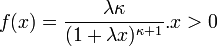
- von Mises:
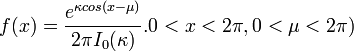
- Generalized Pareto:
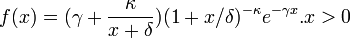
- Triangular:
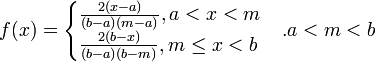
- Kolmogorov-Smirnov:

- Exponential Power:
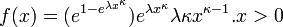
- Lévy distribution:
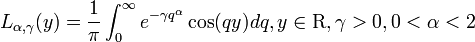
- Modified Power Series distributon:
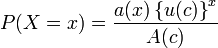 where
where 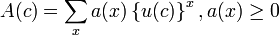
- Positive binomial distribution:
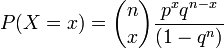 where x = 1,2,...,n
where x = 1,2,...,n
- Basic Lagrangian distribution of the first kind (BLD1):
![P(X=x)={1\over x!} \left[{\partial ^{x-1} \over \partial z^{x-1} } (g(z))^{x} \right]_{z=0}](/socr/uploads/math/8/6/5/865e25b9ac447a7e3e6893adbe278f18.png) where g(z) is pgf , g(0) is not 0
where g(z) is pgf , g(0) is not 0
- General Basic Lagrangian distribution of the first kind (GLD1):
![P(X=0)=f(0) ,
P(X=x)={1\over x!} \left[{\partial ^{x-1} \over \partial z^{x-1} } \left\{(g(z))^{x} {\partial f(z)\over \partial z} \right\}\right]_{z=0} , x>0](/socr/uploads/math/a/0/4/a043797e30ed8822769d249305794d55.png) Where f(z) and g(z) are pgf ,
Where f(z) and g(z) are pgf , ![\left[{\partial ^{x-1} \over \partial z^{x-1} } \left\{(g(z))^{x} {\partial f(z)\over \partial z} \right\}\right]_{z=0} >0](/socr/uploads/math/6/3/8/638f3a1a05a20ea42ad3efacd06413d8.png) for
for 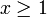
- Binomial-delta distribution:
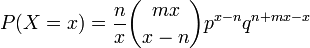 for
for 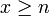
- Binomial-Poisson distribution:
![P(X=x)=e^{-M} {(Mq^{m} )^{x} \over x!} {}_{2} F{}_{0} [1-x,-mx;{p\over Mq} ]](/socr/uploads/math/d/b/5/db5d993b405efa1cb57cf750e16b9e6f.png) , for
, for 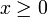
- Binomial-negative-binomial distribution:
![P(X=x)={\Gamma (k+x)\over x!\Gamma (x)} Q^{-k} \left({Pq^{m} \over Q} \right)^{x} {}_{2} F_{1} [1-x,-mx;1-x-k;{-pQ\over qP} ]](/socr/uploads/math/0/7/4/074fb762223b64975f3df34a10fe9dd4.png) for
for 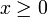
- _Distribution.html Poisson-delta distribution:
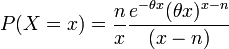 for
for 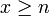
- Poisson-Poisson distribution(also called "Generalized Poisson distribution"): P(X = x) = M(M + θx)x − 1e − (M + θx) / x! for
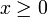
- Poisson-binomial distribution:
![P(X=x)={(\theta x)^{x-1} \over x!} e^{-\theta x} npq^{n-1} {}_{2} F_{0} [1-x,1-n;{p\over \theta qx} ] , x\ge 1](/socr/uploads/math/1/8/d/18ddac41e5953378383b73e12b0edead.png)
- Poisson-negative-binomial distribution:
![P(X=x)={(\theta x)^{x-1} \over x!} e^{-\theta x} kPQ^{-k-1} {}_{2} F_{0} [1-x,1+k;{-P\over \theta Qx} ] , x\ge 1](/socr/uploads/math/2/a/3/2a3ee8ba0eec2960e245f63d7710d3c2.png)
- Negative-binomial-delta distribution:
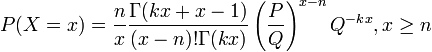
- Negative-binomial-Poisson distribution:
![P(X=x)={e^{-M} M^{x} \over x!} Q^{-kx} {}_{2} F_{0} [1-x,kx;-;{-P\over MQ} ]](/socr/uploads/math/f/b/5/fb5579bf74bcaf2d86ca89c51ed8ff34.png) , for
, for 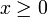
- Negative-binomial-binomial distribution: P(X = 0) = qn ,
![P(X=x)=npq^{n-1} {\Gamma (kx+x-1)\over x!\Gamma (kx)} \left({P\over Q} \right)^{x-1} Q^{-kx} {}_{2} F_{1} [1-x,1-n;2-x-kx;{-pQ\over Pq} ]](/socr/uploads/math/f/1/9/f19a5cb590e1805a74f2af88c55164c2.png) for
for 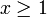
- Negative-binomial-negative-binomial distribution:
![P(X=x)=(Q')^{-M} \left({P'\over Q'Q^{k} } \right)^{x} {\Gamma (M+x)\over x!\Gamma (M)} {}_{2} F_{1} [1-x,kx;1-M-x;{PQ'\over P'Q} ]](/socr/uploads/math/6/d/5/6d59a48095b41ea3d13f5432923374cf.png) for
for 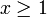
- Weight binomial distribution:
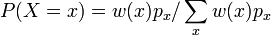
- Positive Poisson distribution (conditional Poisson distribution): P(X = x) = (eθ − 1) − 1θx / x!,x = 1,2,......
- Left-truncated Poisson distribution:
![P(X=x)={e^{-\theta } \theta ^{x} \over x!} \left[1-e^{-\theta } \sum _{j=0}^{r_{1} -1}{\theta ^{j} \over j!} \right]^{-1} , x=r_{1} ,r_{1} +1,...](/socr/uploads/math/8/0/7/8078fdd513a5fa44d305ca3c13f7fdf8.png)
- Right-truncated Poisson distribution:
![P(X=x)={\theta ^{x} \over x!} \left[\sum _{j=0}^{r_{2} }{\theta ^{j} \over j!} \right]^{-1} , x=0,1,...,r_{2}](/socr/uploads/math/9/7/1/9714d03be11d54125fd92b93d05d4e8c.png)
- Doubly-truncated Poisson distribution:
![P(X=x)={\theta ^{x} \over x!} \left[\sum _{j=r_{1} }^{r_{2} }{\theta ^{j} \over j!} \right]^{-1} , x=r_{1} ,r_{1} +1,...,r_{2} , 0<r_{1} <r_{2}](/socr/uploads/math/d/9/d/d9d9957272d113cd458a79ff4b932c79.png)
- Misrecorded Poisson distribution:
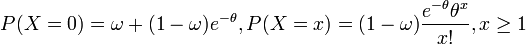
Transformations
- Standard Normal to General Normal Transformation:
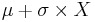
- General Normal to Standard Normal Transformation:
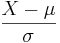
- Standard Normal to Chi Transformation:
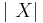
- Standard Normal to Chi-Square Transformation:
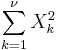
- Gamma to General Normal Transformation:
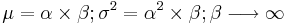
- Gamma to Exponential Transformation: The special case of
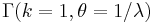 is equivalent to exponential Exp(λ).
is equivalent to exponential Exp(λ).
- Gamma to Beta Transformation:
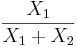 .
.
- Student's T to Standard Normal Transformation:
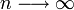
- Student's T to Cauchy Transformation:
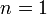
- Cauchy to General Cauchy Transformation:
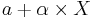
- General Cauchy to Cauchy Transformation:
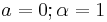
- Fisher's F to Student's T:
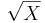
- Student's T to Fisher's F: X2
- Bernoulli to Binomial Transformation:
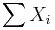 (iid)
(iid)
- Binomial to Bernoulli Transformation:
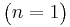
- Binomial to General Normal Transformation:
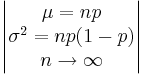
- Binomial to Poisson Transformation:
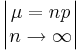
- Multinomial to Binomial Transformation:
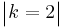
- Negative Binomial to Geometric Transformation:
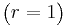
- Erlang to Exponential Transformation:
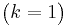
- Erlang to Chi-Square Transformation:
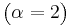
- Laplace to Exponential Transformation:
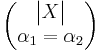
- Exponential to Laplace Transformation:

- Beta to Arcsine Transformation:
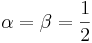
- Noncentral Student's T to Normal Transformation:
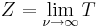
- Noncentral Student's T to Student's T Transformation:
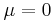
- Standard Uniform to Pareto Transformation:
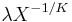
- Standard Uniform to Benford Transformation:
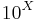
- Standard Uniform to Exponential Transformation:
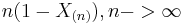
- Standard Uniform to Log Logistic Transformation:
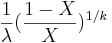
- Standard Uniform to Standard Triangular Transformation: X1 − X2
- Standard Uniform to Logistic Exponential Transformation:
![\frac{log[1+(\frac{X}{1-X})^{1/K}]}{\lambda}](/socr/uploads/math/b/b/1/bb14e96da3be11b8bee63fcfbb54fefa.png)
- Standard Uniform to Beta Transformation: If X has a standard uniform distribution,
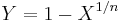 has a beta distribution
has a beta distribution
- Beta to Standard Uniform Transformation: β = γ = 1
- Continuous Uniform to Standard Uniform Transformation:
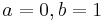
- Pareto to Exponential:
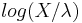
- Logistic Exponential to Exponential:
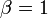
- Zipf to Discrete Uniform:
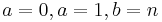
- Discrete Uniform to Rectangular:
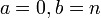
- Poisson to Normal:
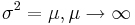
- Binomial to Poisson:
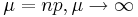
- Gamma to Inverted Gamma:
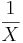
- Fisher-Tippett to Gumbel:
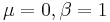
- Hypergeometric to Binomial:
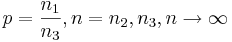
- Log-Normal to Normal:
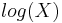
- Normal to Log-Normal:
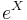
- Log-Normal to Gibrat's:
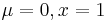
- Cauchy to Standard Cauchy:
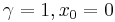
- Standard Cauchy to Cauchy:
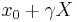
- Standard Cauchy to Hyperbolic Secant:
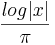
- Beta to Standard Power:
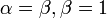
- Power series to Pascal:
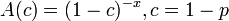
- Gamma Poisson to Pascal:
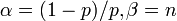
- Poisson to Gamma Poisson:
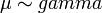
- Discrete uniform to Rectangular:
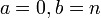
- beta binomial to rectangular:
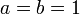
- beta binomial to negative hypergeometric:
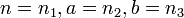
- Zipf to Zeta:
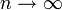
- Power series to Logarithm:
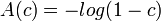
- Power series to Poisson:
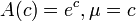
- Pascal to Beta pascal:
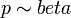
- pascal to poisson:
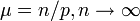
- binomial to beta binomial:
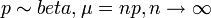
- negative hypergeometric to binomial:
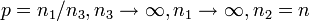
- Polya to Binomial:
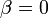
- Pascal to geometric:
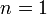
- geometric to pascal:
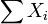
- discrete weibull to geometric:
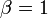
- pascal to normal:
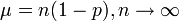
- normal to standard normal:
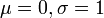
- normal to noncentral_chi-square:
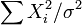
- Normal to Chi-square:
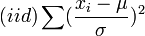
- Beta to Normal:
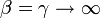
- Normal to Gamma-normal:
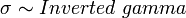
- Standard Normal to Standard Cauchy:
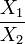
- Inverse Gaussian to Standard normal:
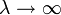
- Noncentral chi-square to Chi-square:
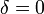
- Gamma to Log gamma:
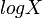
- Generalized gamma to Log normal:
- Generalized gamma to Gamma:
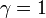
- Inverse Gaussian to Standard Wald:
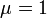
- Inverse Gaussian to Chi-square:
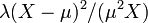
- Chi-square to Chi:
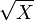
- Chi-square to F:
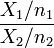
- F to Chi-square:
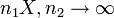
- Exponential to Chi-square:
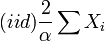
- Chi-square to Exponential:
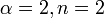
- Chi-square to Erlang:
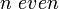
- Gamma to Chi-square:
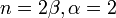
- Beta to Standard Uniform:
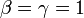
- Gamma to Erlang:
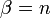
- Gamma to Inverted Beta:
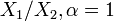
- Beta to Inverted Beta:
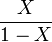
- Cauchy to Arctangent:
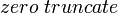
- Hypoexponential to Erlang:
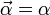
- Exponential to Hypoexponential:
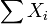
- Erlang to Exponential:
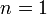
- Makeham to Gompertz:
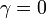
- Doubly noncentral t to Noncentral t:
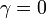
- Exponential to F:
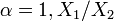
- Noncentral F to F:
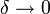
- Exponential to Hyperexponential:
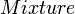
- Hyperexponential to Exponential:
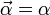
- IDB to Exponential:
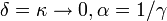
- Exponential to Rayleigh:
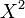
- Weibull to Exponential:
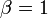
- Exponential to Weibull:
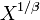
- Muth to Exponential:
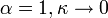
- Standard uniform to Gompertz:
![\frac{log[1-(log X)(log \kappa)/\delta]}{log \kappa}\](/socr/uploads/math/c/6/3/c634f06f234a2c186bdf00f16de3806c.png)
- Standard uniform to Exponential Power:
![[log(1-log(1-X))/\gamma]^{1/\kappa}\](/socr/uploads/math/6/1/9/61957bb86a86f0d6f37a2324154e131a.png)
- Error to Laplace:
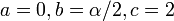
- Laplace to Error:
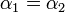
- Standard uniform to log logistic:
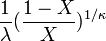
- Standard uniform to Standard triangular:
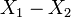
- Standard uniform to uniform:
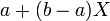
- Standard uniform to standard power:
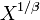
- Standard power to standard uniform:
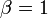
- Standard uniform to standard power:
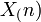
- Minimax to standard power:
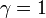
- IDB to Rayleigh:
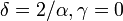
- Power to Standard Power:
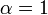
- Weibull to Rayleigh:
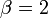
- Generalized Pareto to Pareto:
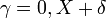
- Triangular to standard triangular:
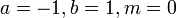
- Weibull to Extreme-value:
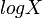
- Log logistic to lomax:
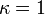
- logistic_Distribution.html Lomax to log logistic:
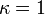
- Log logistic to logistic:
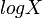
- TSP to triangular:
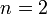
- von Mises to Uniform:
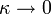
- Lévy to Cauchy:
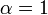
- Lévy to Gaussian:
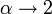
- Modified Power Series to Power series:
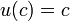
- BLD1 to Geometric:
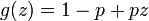 where
where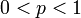
- BLD1 to Borel-Tanner:
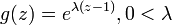
- GLD1 to Binomial:
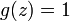 and
and 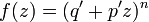 where
where 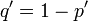 ,
, 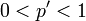 , and n is positive integer.
, and n is positive integer.
- GLD1 to Negative binomial:
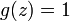 and
and 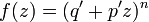 where
where 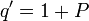 ,
, 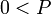 , and
, and 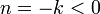
- GLD1 to Binomial-delta:
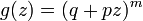 ,
, 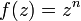 ,
, 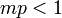
- GLD1 to Binomial-Poisson:
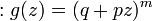 ,
, 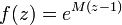 ,
, 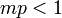
- GLD1 to Binomial-negative-binomial:
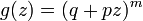 ,
, 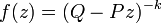 ,
, 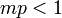
- GLD1 to Poisson-delta:
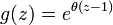 ,
, 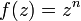 ,
, 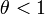
- GLD1 to Poisson-Poisson:
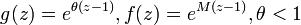
- GLD1 to Poisson-binomial:
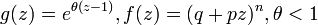
- GLD1 to Poisson-negative-binomial:
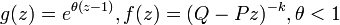
- GLD1 to Negative-binomial-delta:
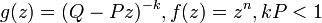
- GLD1 to Negative-binomial-Poisson:
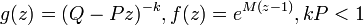
- GLD1 to Negative-binomial-binomial:
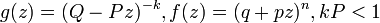
- GLD1 to Negative-binomial-negative-binomial:
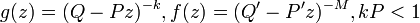
- Chi-Square to Poisson:
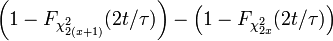 and
and 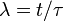
- Left-truncated Poisson to Positive Poisson:
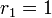
- Doubly-truncated Poisson to Right-truncated Poisson:
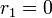
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu
Translate this page:
