SOCR EduMaterials Activities CoinDieExperiment
From Socr
(added the conditional probability as application) |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
: ''P(A={Coin=H})=23/30'' | : ''P(A={Coin=H})=23/30'' | ||
: ''P(B={Die-outcome=5})= 3/30 = 1/10'' | : ''P(B={Die-outcome=5})= 3/30 = 1/10'' | ||
| - | : <math>P(A|B) = P(AB) | + | : <math>P(A|B) = {P(AB) \over P(B)} = {2/30 \over 3/30} = 20/30 \approx P(A) = 23/30</math>. So, here, independence is controlled by making the two dice have the same probability distributions. Altering the distributions of the 2 dice will introduce a dependence between the events ''A'' and ''B''. Try to validate it by this applet simulation. |
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image: SOCR_Activities_CoinDie_Dinov_091208.png|600px]]</center> | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
* SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu | * SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu | ||
{{translate|pageName=http://wiki.stat.ucla.edu/socr/index.php?title=SOCR_EduMaterials_Activities_CoinDieExperiment}} | {{translate|pageName=http://wiki.stat.ucla.edu/socr/index.php?title=SOCR_EduMaterials_Activities_CoinDieExperiment}} | ||
Revision as of 21:47, 12 September 2008
This is an activity to explore the distribution of the die score (Y) when a coin is tossed first.
Open http://www.socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Experiments.html and use the scroll bar to find the Coin Die Experiment. Once you find it, click on the About button and read about the experiment. Below you can see the outcome of 10 runs of the experiment.
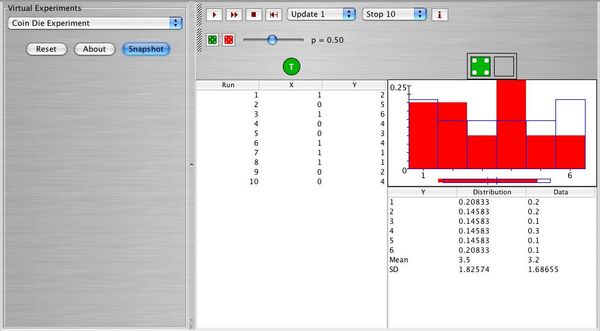
Answer the following questions:
a. There are two random variables (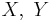 ), one parameter (p) for the coin, and the probability distribution that governs each die (green or red) involved in this experiment. Describe what each one represents.
), one parameter (p) for the coin, and the probability distribution that governs each die (green or red) involved in this experiment. Describe what each one represents.
b. Choose fair coin (p = 0.5), and fair dice (green and red). Perform 100 runs, take a snapshot and comment.
c. Reset. Choose p = 0.8, 1-6 flat for the green die, 3-4 flat for the red die. Construct the probability distribution of Y, compute the mean of Y, and the standard deviation of Y. Verify that they agree with the ones in the applet.
d. Reset. Choose p = 0.2, green fair die, 2-5 flat for red die, perform 100 runs, take a snapshot and comment.
Applications - Conditional Probability
The SOCR Coin-Die Experiment may be used to demonstrate the notion of conditional probability.
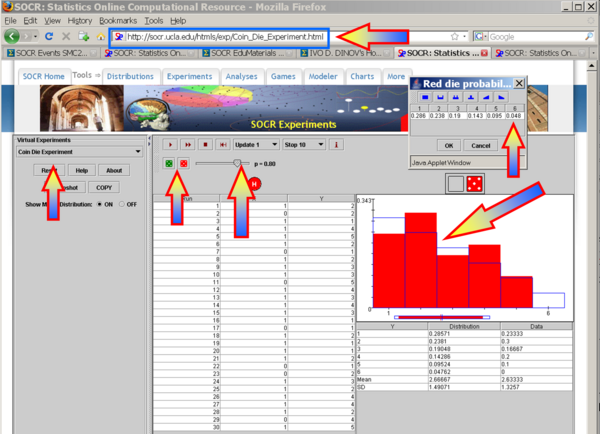
Go to the Coin Die Experiment. Here independence of the outcome of the die (event B), relative to the outcome of the coin (event A), is ensured by setting the probabilities of both dice to be identical, see the image below. For example, an experiment of 30 samples provides the following results (note that p=0.8!):
- P(A={Coin=H})=23/30
- P(B={Die-outcome=5})= 3/30 = 1/10
-
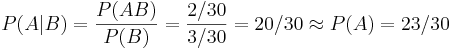 . So, here, independence is controlled by making the two dice have the same probability distributions. Altering the distributions of the 2 dice will introduce a dependence between the events A and B. Try to validate it by this applet simulation.
. So, here, independence is controlled by making the two dice have the same probability distributions. Altering the distributions of the 2 dice will introduce a dependence between the events A and B. Try to validate it by this applet simulation.
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu
Translate this page:
