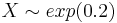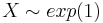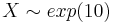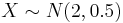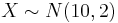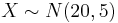SOCR EduMaterials Activities ExpDist
From Socr
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
You can access the applet for the [http://www.socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Distributions.html Exponential Distributions] | You can access the applet for the [http://www.socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Distributions.html Exponential Distributions] | ||
| + | * Graph and print | ||
| + | **<math>X \sim exp(0.2)</math><br> | ||
| + | **<math>X \sim exp(1)</math> <br> | ||
| + | **<math>X \sim exp(10)</math> | ||
| - | + | * Locate the maximum density for each one of these distributions. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | * Find the height of the density at 3 values of <math>X</math> (one near 0, one near the mean, and one towards the tail of the distribution). | ||
| + | * Find one percentile for each of these distributions and record them on the printouts. Verify these percentiles using the formula we discussed in class: | ||
| + | <math>\[ x_p=\frac{ln(1-\frac{p}{100})}{-\lambda}\]</math> | ||
| + | * Compute one cumulative probability for each one of these distributions, show it on the graph, and verify it with the formula: | ||
| + | <math>\[ P(X \le x)=1-e^{-\lambda x} \]</math> | ||
| + | * Graph and print | ||
| + | ** <math>X \sim N(2,0.5)</math> | ||
| + | ** <math>X \sim N(10,2)</math> | ||
| + | ** <math>X \sim N(20,5)</math> | ||
| + | * Find one percentile for each one of these distributions and locate them on the printouts. | ||
| + | * Find one cumulative probability for each one of these distributions and locate them on the printouts. | ||
=='''Exercise 1'''== | =='''Exercise 1'''== | ||
| Line 64: | Line 55: | ||
=='''Exercise 7'''== | =='''Exercise 7'''== | ||
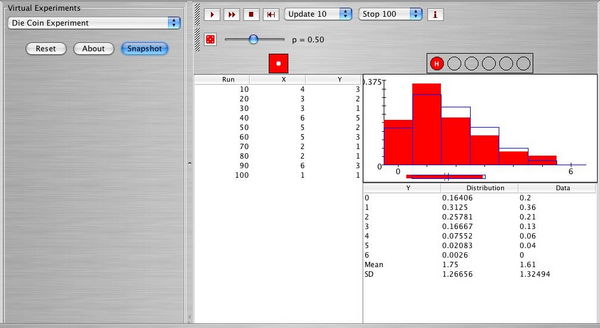
Use SOCR [http://www.socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Experiments.html Experiments] and choose "Die Coin Experiment" to graph and print the empirical distribution of Y when the experiment is performed: | Use SOCR [http://www.socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Experiments.html Experiments] and choose "Die Coin Experiment" to graph and print the empirical distribution of Y when the experiment is performed: | ||
| - | + | * n = 1000 times. | |
| - | + | * n= 10000 times | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<center>[[Image:SOCR_Activities_DieCoinExperiment_Christou_092206_Fig1.jpg |600px]]</center> | <center>[[Image:SOCR_Activities_DieCoinExperiment_Christou_092206_Fig1.jpg |600px]]</center> | ||
Revision as of 17:14, 12 June 2007
Contents |
This is an activity to explore the Exponential Distribution: Learn how to compute probabilities, densities, and percentiles
Description
You can access the applet for the Exponential Distributions
- Graph and print
- Locate the maximum density for each one of these distributions.
- Find the height of the density at 3 values of X (one near 0, one near the mean, and one towards the tail of the distribution).
- Find one percentile for each of these distributions and record them on the printouts. Verify these percentiles using the formula we discussed in class:
Failed to parse (lexing error): \[ x_p=\frac{ln(1-\frac{p}{100})}{-\lambda}\]
- Compute one cumulative probability for each one of these distributions, show it on the graph, and verify it with the formula:
Failed to parse (lexing error): \[ P(X \le x)=1-e^{-\lambda x} \]
- Graph and print
-
- Find one percentile for each one of these distributions and locate them on the printouts.
- Find one cumulative probability for each one of these distributions and locate them on the printouts.
Exercise 1
Construct the joint probability distribution of X and Y.
Exercise 2
Find the conditional expected value of Y given X=5.
Exercise 3
Find the conditional variance of Y given X=5.
Exercise 4
Find the expected value of Y.
Exercise 5
Find the standard deviation of Y.
Exercise 6
Graph the probability distribution of Y.
Exercise 7
Use SOCR Experiments and choose "Die Coin Experiment" to graph and print the empirical distribution of Y when the experiment is performed:
- n = 1000 times.
- n= 10000 times
Exercise 8
Compare the theoretical mean and standard deviation of Y (exercise 4 and 5) with the empirical mean and standard deviation found in exercise 7.
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu
Translate this page: