SOCR EduMaterials Activities GeneralCentralLimitTheorem
From Socr
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=== This activity represents a very general demonstration of the effects of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_limit_theorem Central Limit Theorem (CLT)]. The activity is based on the [[About_pages_for_SOCR_Experiments | SOCR Sampling Distribution CLT Experiment]]. This experiment builds upon a [http://www.ruf.rice.edu/~lane/stat_sim/sampling_dist/ RVLS CLT applet] by extending the applet functionality and providing the capability of sampling from any [[About_pages_for_SOCR_Distributions | SOCR Distribuion]].=== | === This activity represents a very general demonstration of the effects of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_limit_theorem Central Limit Theorem (CLT)]. The activity is based on the [[About_pages_for_SOCR_Experiments | SOCR Sampling Distribution CLT Experiment]]. This experiment builds upon a [http://www.ruf.rice.edu/~lane/stat_sim/sampling_dist/ RVLS CLT applet] by extending the applet functionality and providing the capability of sampling from any [[About_pages_for_SOCR_Distributions | SOCR Distribuion]].=== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| - | * ''' | + | * '''Goals''': The aims of this activity are to |
| + | ** provide intuitive notion of sampling from any process with a well-defined distribution | ||
| + | ** motivate and facilitate learning of the central limit theorem | ||
| + | ** emperically validate that sample-averages of random observations (most processes) follow approximately [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_distribution normal distribution] | ||
| + | ** emperacally demonstrate that the ''sample-average'' is special and other sample statistics (e.g., median, variance, range, etc.) generally do not have distributions that are normal | ||
| + | ** illustrate that the expectation of the sample-average equals the population mean (and the sample-average is typically a good measure of centrality for a population/process) | ||
| + | ** show that the variation of the sample average rapidly decreases and the sample size increases (<math>~1/\sqrt(n)</math>) | ||
<center>[[Image:SOCR_Activities_CardCoinSampling_Dinov_092206_Fig1.jpg|300px]]</center> | <center>[[Image:SOCR_Activities_CardCoinSampling_Dinov_092206_Fig1.jpg|300px]]</center> | ||
Revision as of 20:42, 22 January 2007
SOCR Educational Materials - Activities - SOCR General Central Limit Theorem (CLT) Activity
This activity represents a very general demonstration of the effects of the Central Limit Theorem (CLT). The activity is based on the SOCR Sampling Distribution CLT Experiment. This experiment builds upon a RVLS CLT applet by extending the applet functionality and providing the capability of sampling from any SOCR Distribuion.
- Goals: The aims of this activity are to
- provide intuitive notion of sampling from any process with a well-defined distribution
- motivate and facilitate learning of the central limit theorem
- emperically validate that sample-averages of random observations (most processes) follow approximately normal distribution
- emperacally demonstrate that the sample-average is special and other sample statistics (e.g., median, variance, range, etc.) generally do not have distributions that are normal
- illustrate that the expectation of the sample-average equals the population mean (and the sample-average is typically a good measure of centrality for a population/process)
- show that the variation of the sample average rapidly decreases and the sample size increases (
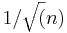 )
)
- SOCR Home page: http://www.socr.ucla.edu
Translate this page:
